Ad-Hoc iOS App Distribution Notes
4 minutes reading time
#Ad-hoc iOS distribution.
Ad hoc distribution lets developers install internal builds of iOS apps on up to 100 registered devices of a type per year. My clients mostly run video software on iPhones and iPads. This page contains notes I used when adding devices and distributing apps to beta users.
#Register a device
Devices are added to your account at https://developer.apple.com. In order to add a device, you need its UDID. The UDID is different from the Serial Number or IEMI. There are several ways of obtaining the UDID. I use Device Manager on Windows 10 and Finder on macOS.
#Getting a UDID on Windows
- Connect your iOS device to a Windows machine's USB port
- Open Device Manager
- expand "Universal Serial Bus devices"
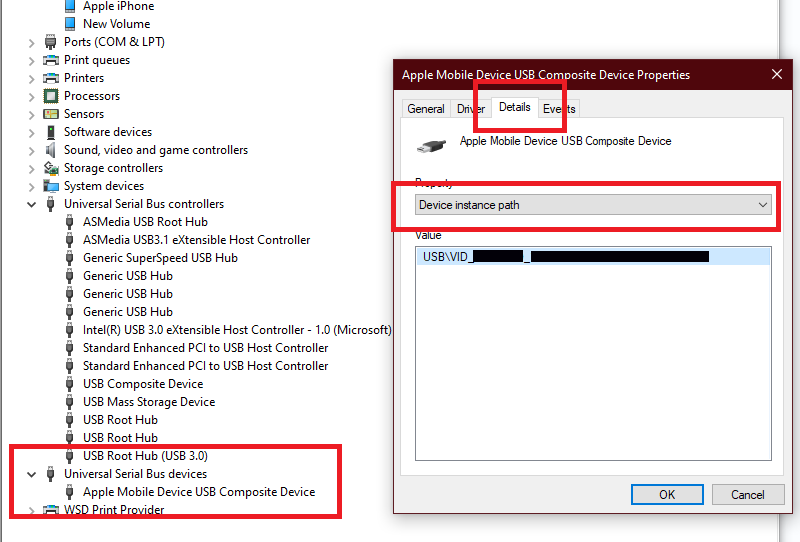
- get the properties for "Apple Mobile Device USB composite Deice"
- go to the "Details" tab
- select "Device Instance path"
#Getting a UDID on macOS
- Connect your iOS device to your mac's USB port
- Open Finder
- Select your device on the left,
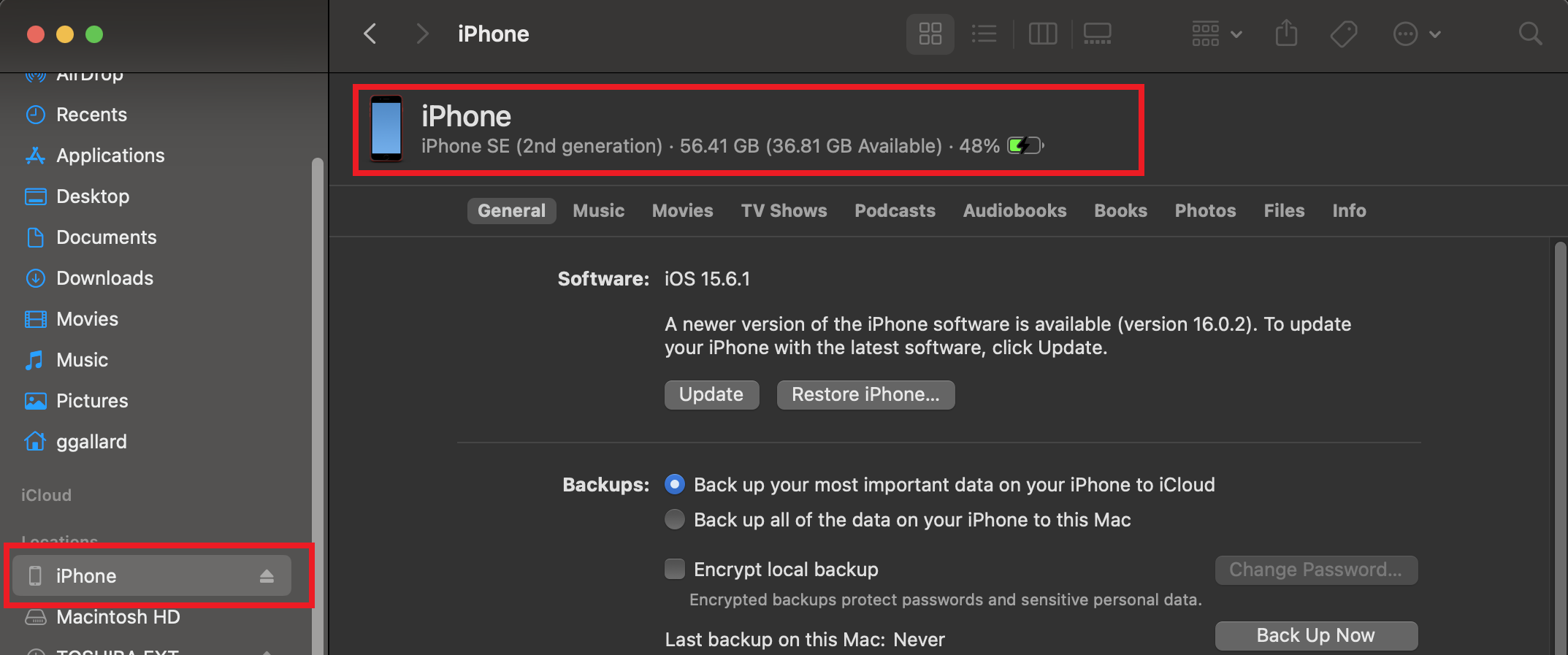
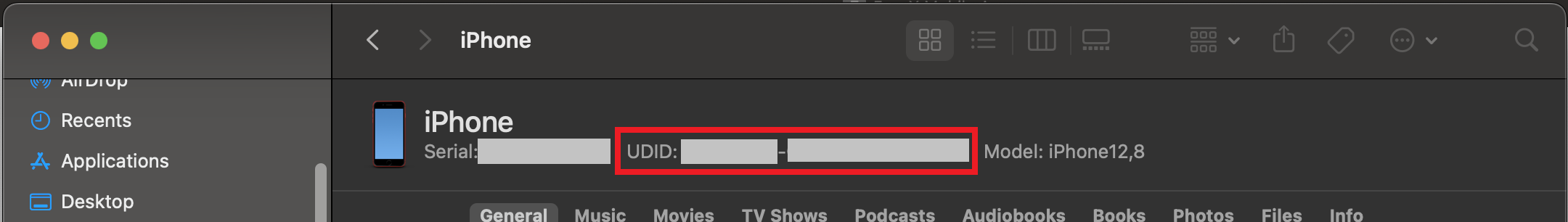
- The device name is displayed at the top. Click at it to get the UDID.
#Adding to your dev pool
Log into your developer account at Apple and add to the device list
#Generate .ipa With XCode
- In your XCode window change the target to
Any iOS Device (arm64)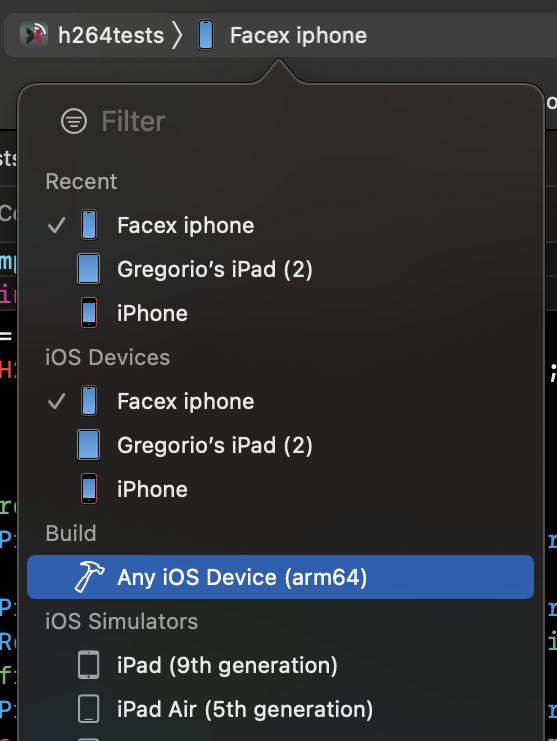
- Open the
Productmenu and selectArchive. This tells XCode to build an archive for distribution.
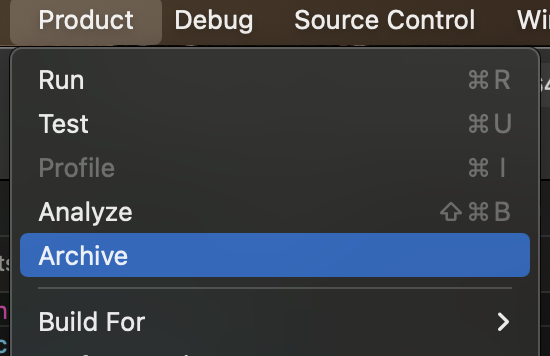 This may take awhile.
This may take awhile.
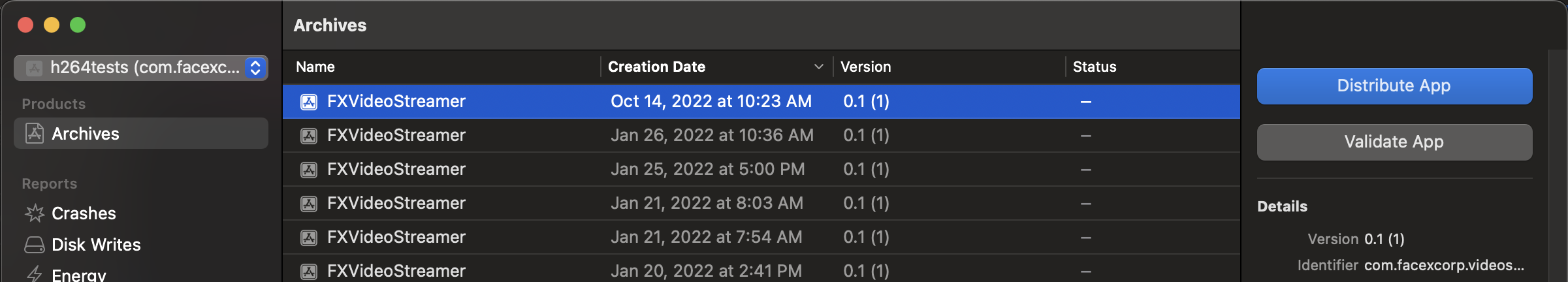
- When the archive is ready, XCode will open a dialog box listing the archives it has created. Select the Archive you just created and press the 'Distribute App' button.
- In the "Select a method of distribution" dialog box select 'Ad Hoc' and press
Next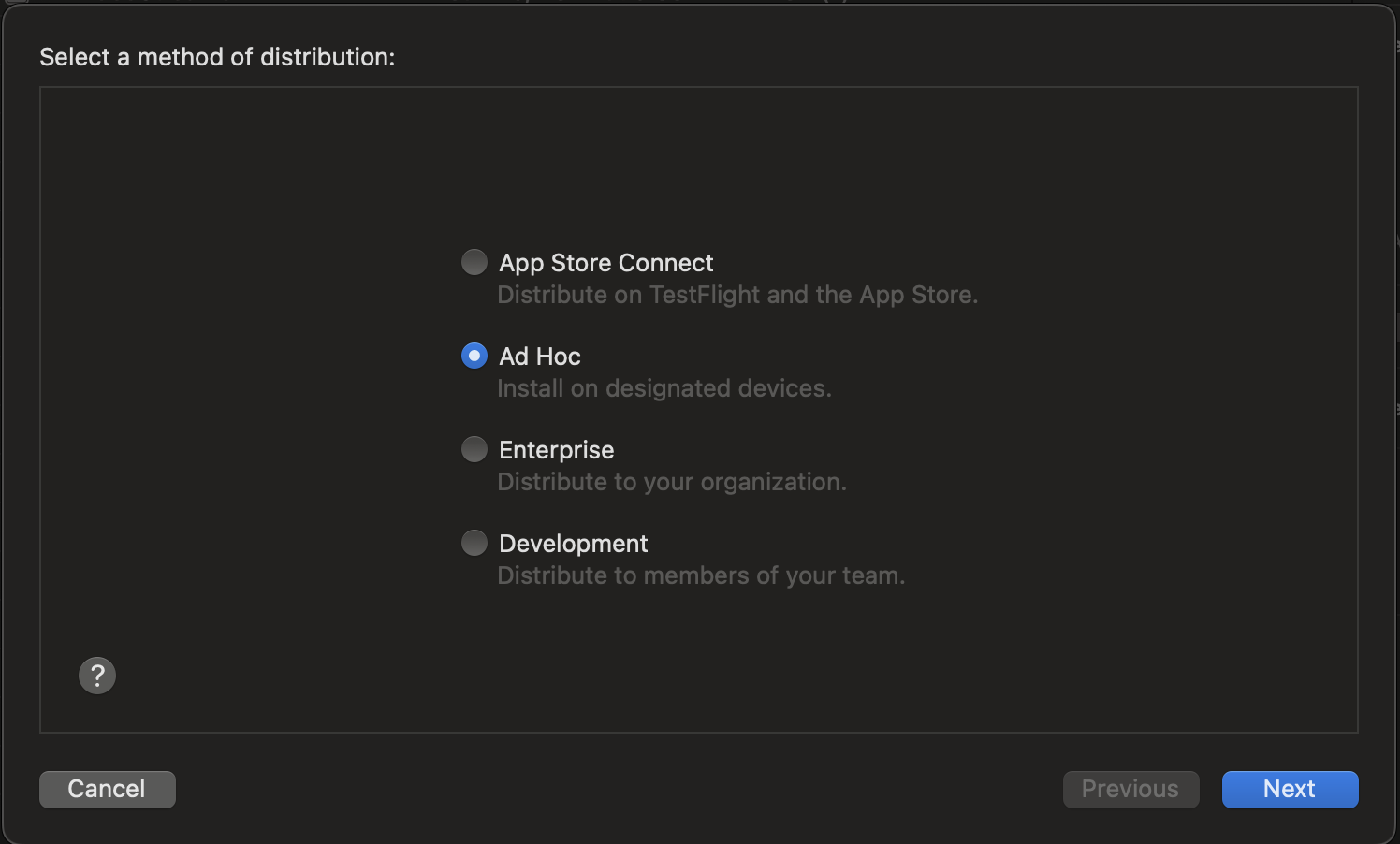
- In the "Ad Hoc distribution option:" dialog box, set the following values.
- App Thinning: None
- Additional Options:
- Strip Swift Symbols : checked
- Include manifest for over-the-air installation: checked
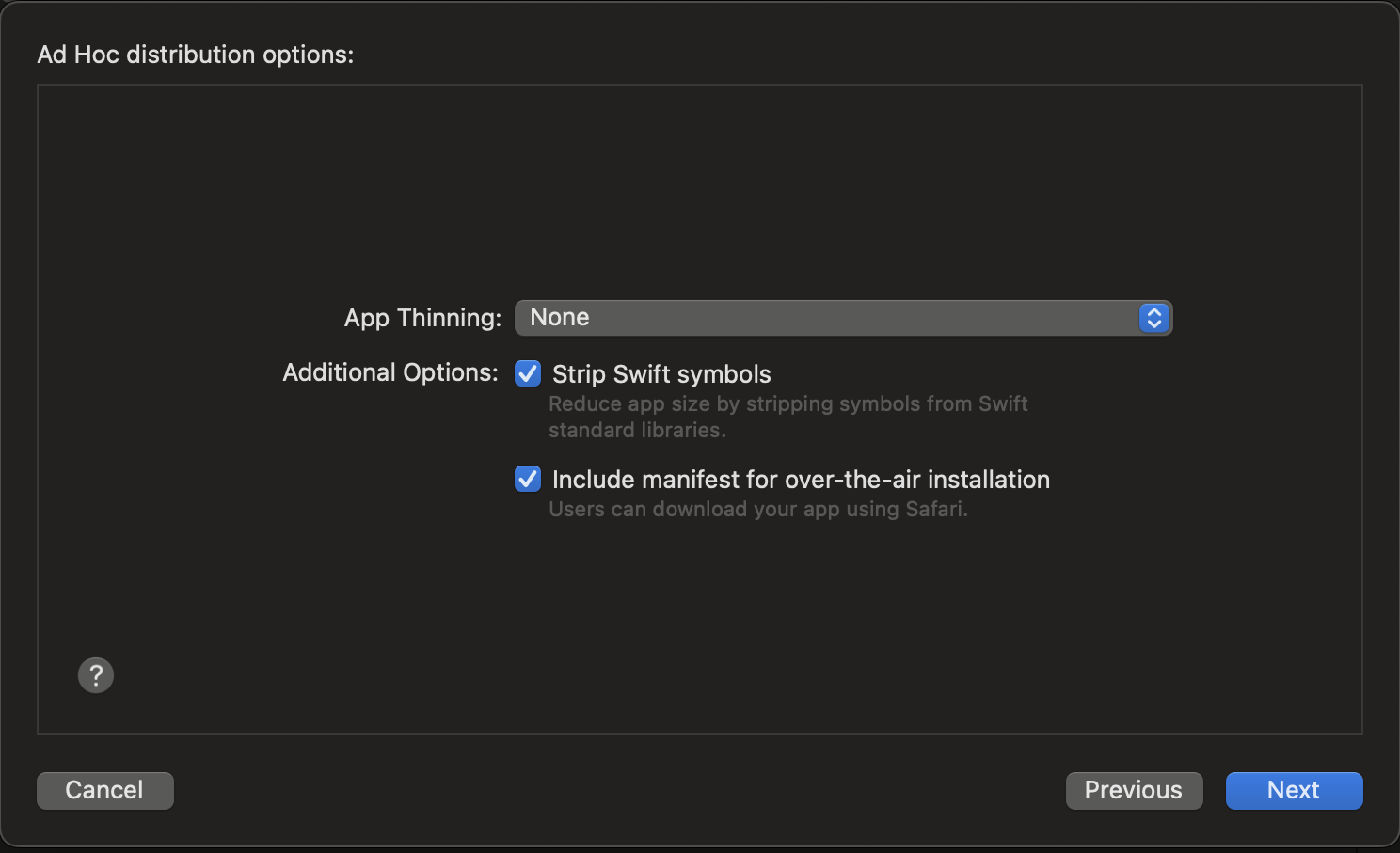 and press
and press Next
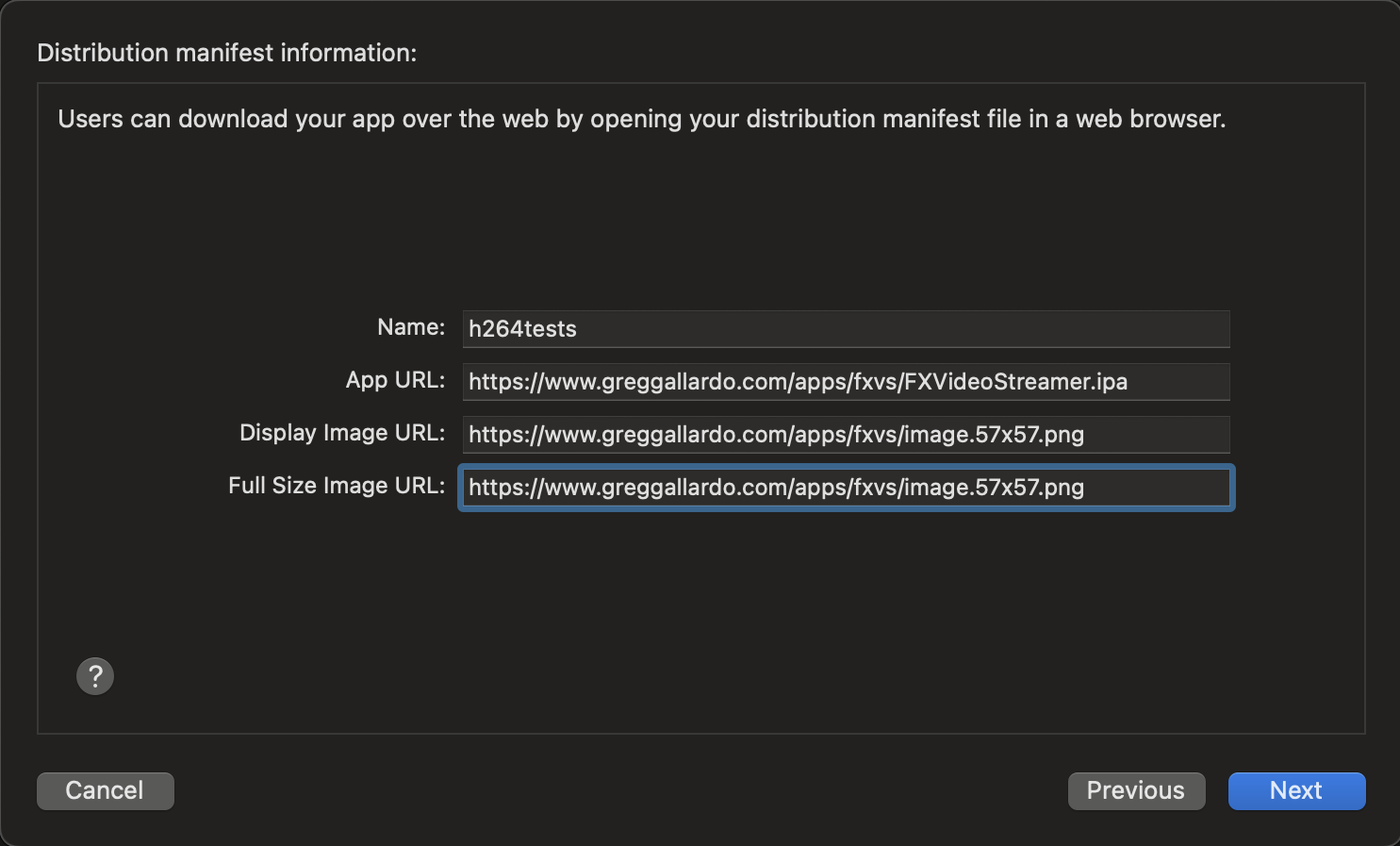
- In the "Distribution manifest information:" dialog set the name and URLs for each field. In my case, I have the following values.
- Name: FX Video Streamer
- App URL: https://www.greggallardo.com/apps/fxvs/FXVideoStreamer.ipa
- Display Image URL: https://www.greggallardo.com/apps/fxvs/image.57x57.png
- Full Size Image URL: https://www.greggallardo.com/apps/fxvs/image.512x512.png The URLS must match the location of the files in your web server.
 and press
and press Next
- In the "Re-sign" dialog box select 'Automatically Manage Signing' and press
Next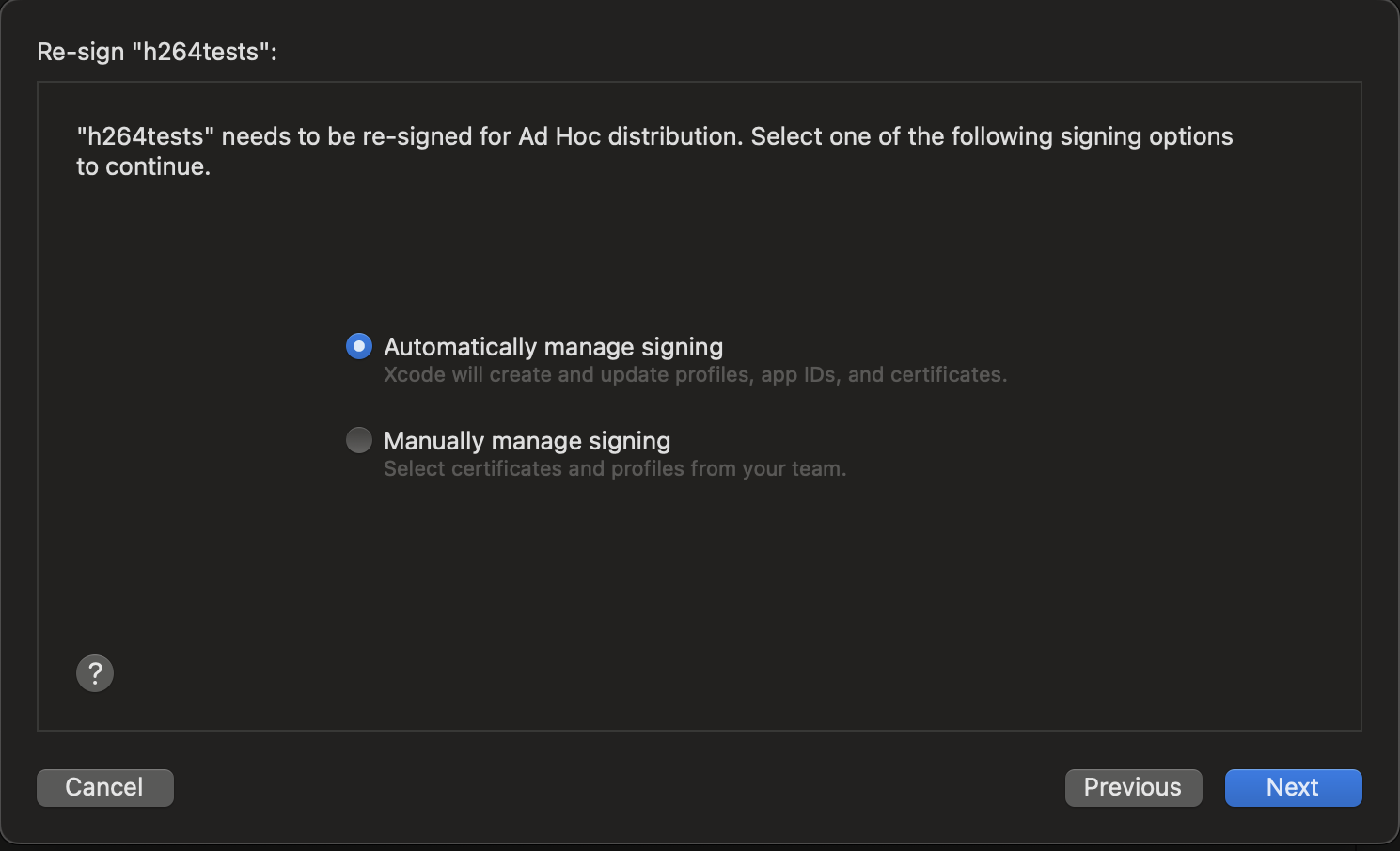 XCode will connect with Apple's servers to sign the distribution files. This may take a long while.
XCode will connect with Apple's servers to sign the distribution files. This may take a long while.
When it finishes, it will list information about the App. Press Export to select the output folder location.
After exporting the app, you'll have a folder containing the files for distribution. Transfer the generated files to your webserver for distribution. On your server, you'll need to make sure names match the files mentioned in manifest.plist.
#Ad-Hoc Web Server Deployment
You can use any web server to deploy the app. For simple deployments, I just use Python 3.
A quick and dirty web server with SSL can look like this:
=
=
Use <a href="itms-services: to create a link to download your app to an iOS device.
Test Mobile Apps
Test Video Stream App
Install App
The directory structure for this server looks like this: